NEID RV Eras¶
Overview¶
The NEID spectrograph has undergone several significant events which have the potential to impart constant offsets in the RV streams. We refer to these time periods as eras. Users who are searching for signals in the RV time series data should add additional constant terms to their fits, bounded by these eras. Please note that the RV offsets between eras may be dependent on a star’s spectral type.
Important dates defining NEID eras are:
Era 1: November 6, 2019 - November 30, 2019 - Commissioning
This era covers the initial thermal cycle of NEID post delivery to WIYN. It ends with a CCD warmup event to mitigate ice buildup.
Era 2: November 30, 2019 - February 27, 2020 - Commissioning
This era covers most of the initial commissioning activities post delivery of the instrument to Kitt Peak. The era begins following a CCD temperature cycle that was done to mitigate ice buildup and ends with the warmup needed to carryout the CCD getter intervention.
Era 3: February 27, 2020 - March 31, 2020 - Commissioning
This era covers the timespan following the NEID CCD getter intervention vacuum cycle and the Covid-19 shutdown. No science data was taken during this era.
Era 4: October 26, 2020 - June 16, 2022 - Science Run 1
This era covers the timespan following recovery from the Covid-19 shutdown up until the Contreras fire. This era includes both commissioning and science data.
Era 5: October 18, 2022 - August 19, 2024 - Science Run 2
This era covers the timespan following recovery from the Contreras fire. The instrument was vacuum pumped starting on October 18, which sets the beginning of this era. This era includes shared-risk and standard science data.
Era 6: August 24, 2024 - December 8, 2025 - Science Run 3
This era covers the timespan following Summer 2024 engineering. The LFC photonic crystal fiber (PCF) was upgraded during the week of August 24, which substantially broadened its wavelength range. After this change, LFC light is used by the pipeline to calculate wavelength solutions and instrument drift down to zero-indexed order 40, approx 458nm, (v1.4.1). Prior this change, the ThAr master solution was used to define the wavelength solutions blueward of order index 55 (approx 500 nm), based on drift calculated from the LFC order 57 redward. This change in order basis resulted in a zero point shift in the algorithm that manifests as a small overall RV shift. This change only affects data processed with DRP v1.4.0 and later
Era 7: December 9, 2025 - current - Science Run 4
This era covers the timespan following a failure in the temperature control system that caused the instrument to significantly warm up. The amplitude and extent of the RV offset caused by this instability is still being investigated, but data in this range must be treated as a new era. Data over the timespan of December 9 to December 21, 2025 should be treated with extreme caution and are possibly not usable for any science. Data over the timespan of December 21, 2025 to January 1, 2026 are not usable for high precision science because the instrument was still stabilizing.
Note: All science data available in the NEID archive was taken as part of Eras 4, 5, 6, or 7. Era 1-3 contain commissioning data that is not processed by the current pipeline.
Candiate RV Eras¶
The NEID SpecSoft team is investigating another potential RV era in the NEID data between October 26, 2020 and roughly August 1, 2021. This would split RV Era 4 in half. There seems to be a tentative zero-point offset on the order of a m/s in the RVs and a small offset in the FWHM of the cross-correlation functions. We will update users soon regarding how to address this candidate era.
Example of RV Eras Across Observed Time Series¶
Below is an RV time series of Tau Ceti (an RV standard star observed regularly by NEID) showing RVs derived with both DRP v1.3 and 1.4.0. We use this to illustrate differences in derived RVs between DRP versions and RV eras
NOTE: Users must take care when analyzing RV time series. You cannot mix RVs produced by different versions of the DRP, and RVs from different eras must be treated as separate data sets.
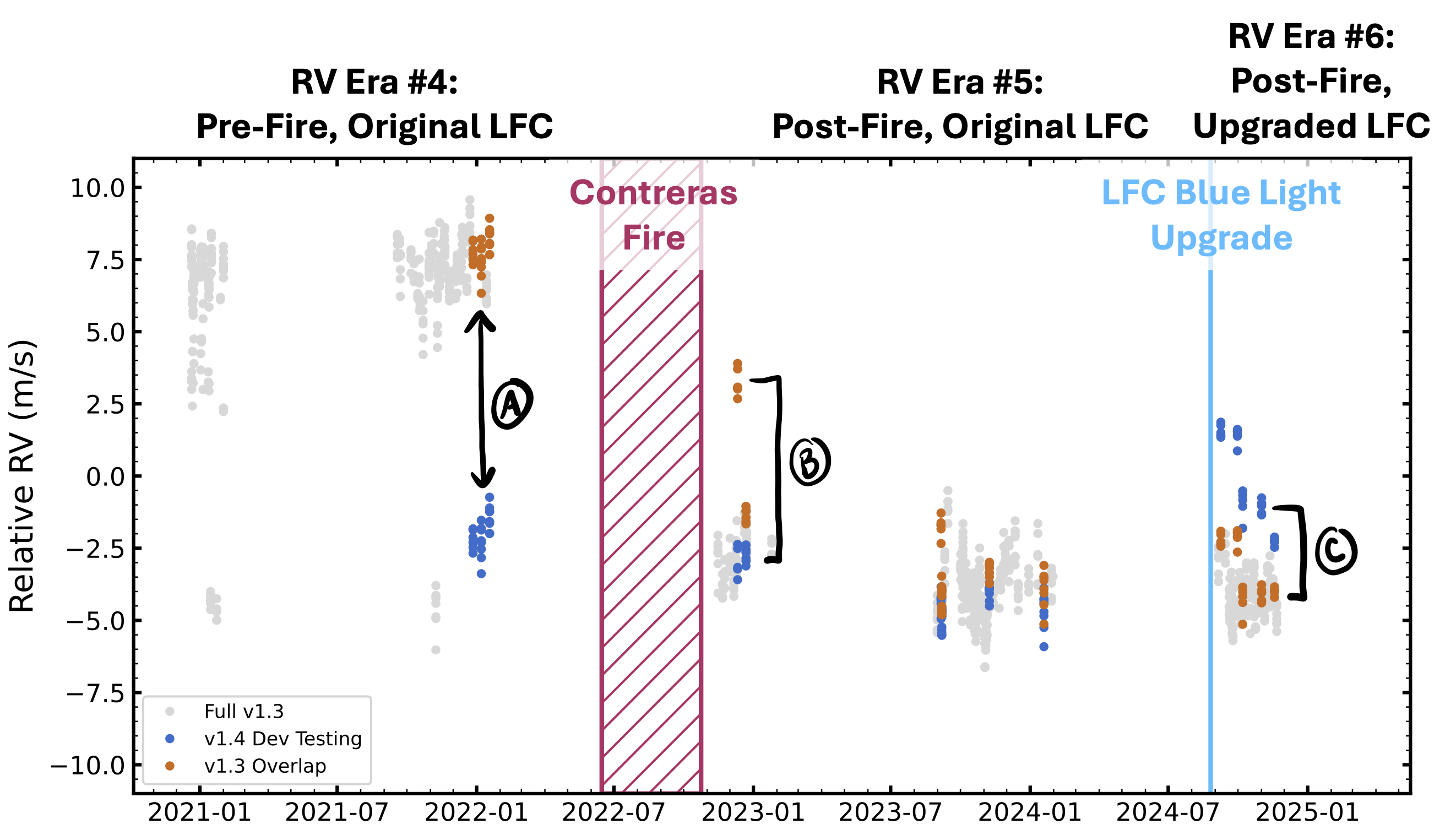
In the above plot: the gray points are the full RV time series of Tau Ceti produced by DRP v1.3, the blue points are a selection of RVs produced while testing DRP v1.4.0, and the orange points simply highlight the DRP v1.3 RVs from the same nights used for testing v1.4.
The time range of the Contreras fire is shown by the red hatched region, and the light blue vertical line shows the first date on which spectra were taken with the upgraded LFC PCF that extends its spectral grasp to roughly 420 nm.
We highlight three important parts of the time series A, B, and C to explain differences in RVs produced by different DRP versions and across different eras:
There is an offset between data in RV Era #4 produced by DRP v1.4.0 and previous versions of the DRP. This is because the masterfiles used to measure the zero-point drift relative to the ThAr master wavelength solution have been corrected. The amplitude of this offset will vary based on a star’s spectral type. While different eras still need to be treated differently, you can see that RVs in Era #4 with DRP v1.4.0 now more closely agree with RVs in Era #5.
This highlights one night where the vetting of LFC quality has improved the wavelength calibration. The roughly 5 m/s offset in v1.3 RVs on that night relative to the rest of the time series is due to a low quality LFC frame. The vetting introduced in v1.4.0 removes that frame from the wavelength calibration, resulting in high precision RVs agreeing with the rest of the time series. While this night was not marked as a fallback in v1.3, it nevertheless is improved in v1.4.0.
This last set of data shows RVs after the installation of the new blue-capable LFC fiber. There is an offset relative to the other RV eras (and to RVs produced by DRP v1.3) because the set of orders for which the LFC is used to derive the wavelength solution has expanded. The new DRP v1.4.0 RVs are of similar quality, but must be treated as a new RV era with its own offset. This offset will also be spectral type dependent.
Last Updated: 2026-01-30, CFB
